What is AWS?
AWS (Amazon Web Services) is a comprehensive, evolving cloud computing platform provided by Amazon that includes a mixture of infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), platform-as-a-service (PaaS) and packaged-software-as-a-service (SaaS) offerings. AWS services can offer an organization tools such as compute power, database storage and content delivery services.
Amazon.com Web Services launched its first web services in 2002 from the internal infrastructure that Amazon.com built to handle its online retail operations. In 2006, it began offering its defining IaaS services. AWS was one of the first companies to introduce a pay-as-you-go cloud computing model that scales to provide users with compute, storage or throughput as needed.
AWS offers many different tools and solutions for enterprises and software developers that can be used in data centers in up to 190 countries. Groups such as government agencies, education institutions, non-profits and private organizations can use AWS services.
How AWS works
AWS is separated into different services; each can be configured in different ways based on the user’s needs. Users can see configuration options and individual server maps for an AWS service.
Availability
AWS provides services from dozens of data centers spread across 87 availability zones (AZs) in regions across the world. An AZ is a location that contains multiple physical data centers. A region is a collection of AZs in geographic proximity connected by low-latency network links.
A business will choose one or multiple AZs for a variety of reasons, such as compliance, proximity to end customers and availability optimization. For example, an AWS customer can spin up virtual machines (VMs) and replicate data in different AZs to achieve a highly reliable cloud infrastructure that is resistant to failures of individual servers or an entire data center.
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) is a service that provides virtual servers – called EC2 instances — for compute capacity. The EC2 service offers dozens of instance types with varying capacities and sizes. These are tailored to specific workload types and applications, such as memory-intensive and accelerated-computing jobs. AWS also provides Auto Scaling, a tool to dynamically scale capacity to maintain instance health and performance.
Storage
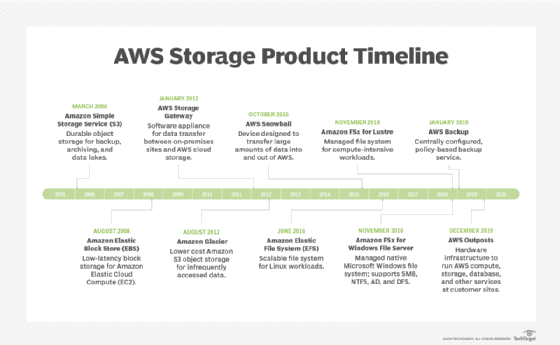
Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) provides scalable object storage for data backup, collection and analytics. An IT professional stores data and files as S3 objects — which can range up to five gigabytes – inside S3 buckets to keep them organized. A business can save money with S3 through its Infrequent Access storage class or by using Amazon Glacier for long-term cold storage.
Amazon Elastic Block Store provides block-level storage volumes for persistent data storage when using EC2 instances. Amazon Elastic File System offers managed cloud-based file storage.
A business can also migrate data to the cloud via storage transport devices, such as AWS Snowball, Snowball Edge and Snowmobile, or use AWS Storage Gateway to let on-premises apps access cloud data.
Databases and data management
The Amazon Relational Database Service includes options for Oracle, MariaDB, MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server and a proprietary high-performance database called Amazon Aurora. It provides a relational database management system for AWS users. AWS also offers managed NoSQL databases through Amazon DynamoDB.
An AWS customer can use Amazon ElastiCache and DynamoDB Accelerator as in-memory and real-time data caches for applications. Amazon Redshift offers a data warehouse, which makes it easier for data analysts to perform business intelligence tasks.
Migration and hybrid cloud
AWS includes various tools and services designed to help users migrate applications, databases, servers and data onto its public cloud. The AWS Migration Hub provides a location to monitor and manage migrations from on premises to the cloud. Once in the cloud, EC2 Simple Systems Manager helps an IT team configure on-premises servers and AWS instances.
Amazon also has partnerships with several technology vendors that ease hybrid cloud deployments. VMware Cloud on AWS brings software-defined data center technology from VMware to the AWS cloud. Red Hat Enterprise Linux for Amazon EC2 is the product of another partnership, extending Red Hat’s operating system to the AWS cloud.
Once applications, databases, servers and data are migrated to the cloud or a hybrid environment, tools like AWS Outposts deliver AWS services and infrastructure across multiple environments.
0 Comments